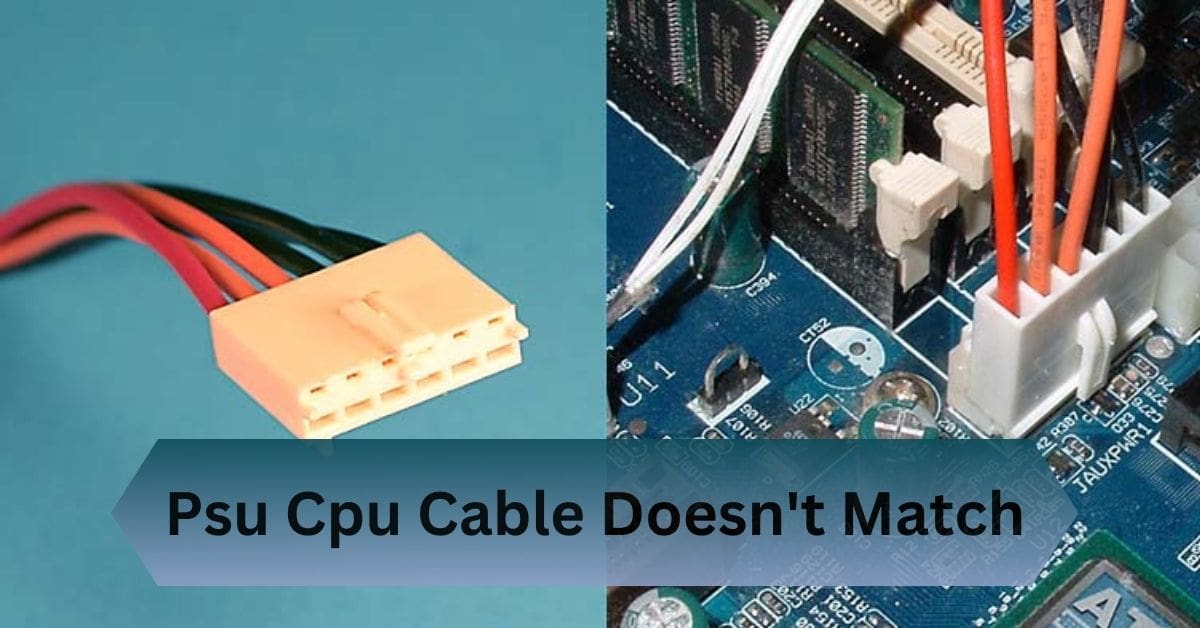
I struggled with my PSU CPU cable not matching the 8-pin connector on my new motherboard. After hours of troubleshooting, I realized my PSU had the wrong cable type. I bought a new PSU to fix the issue and power my system correctly.
Check for 4-pin vs. 8-pin compatibility or modular cable issues if your PSU CPU cable doesn’t match. Ensure you have the correct cable, or consider upgrading the PSU.
Are you frustrated that your PSU CPU cable doesn’t fit? Don’t worry—we can solve the problem quickly with the right cable or a simple PSU upgrade.
Table of Contents
Understanding PSU and CPU Power Requirements
Before diving into why your PSU CPU cable doesn’t match, it’s crucial to understand the role of the PSU (Power Supply Unit) and how it powers your CPU (Central Processing Unit).
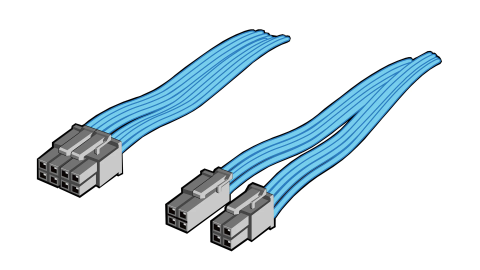
The CPU is your computer’s brain and requires a stable power supply (PSU) to function correctly. The PSU converts AC power from your wall outlet into lower-voltage DC power that your components can use.
Depending on the motherboard’s design and the CPU’s power needs, the motherboard’s CPU power connector typically requires a 4-pin, 8-pin, or sometimes even a 12-pin power cable.
Why does the PSU CPU Cable Not match?
1. Different Connector Types:
The most common cause of mismatching PSU CPU cables is that the connector type does not align with what your motherboard requires. This often occurs because there are multiple standards in use today. Let’s take a closer look at these:
- EPS (8-pin): This is the most common CPU power connector on modern motherboards. It supplies the CPU with ample power and is generally required for high-performance CPUs that demand more electricity.
- 4-pin ATX: Older or lower-power motherboards may still use a 4-pin ATX CPU connector. This supplies less power and is typically sufficient for budget builds or older systems.
- 4+4-pin Configuration: Many modern PSUs feature a 4+4-pin connector, which can be split into two 4-pin connectors. This is designed to be backward compatible with motherboards requiring only a 4-pin connection while supporting 8-pin configurations.
The Mismatch:
A mismatch can happen if your PSU only offers a 4-pin ATX connector while your motherboard requires an 8-pin EPS connector. Conversely, you might have an 8-pin connector, but your motherboard only has a 4-pin socket.
In some cases, newer motherboards might even require additional CPU power connectors (such as an additional 4-pin or 8-pin socket), which some PSUs may not support out of the box.
Read Also: Cha Fan Vs Cpu Fan – From Airflow To Temperature Control!
2. Modular PSU Cables from Different Brands:
Another common problem arises when using modular PSUs. These types of PSUs allow you to connect only the cables you need, leading to a cleaner build. However, the flexibility of modular PSUs also introduces a new potential issue: incompatible cables.
- Brand-Specific Wiring: PSU manufacturers may use the same connector shapes but wire the pins differently. This means that while the connector from one brand might physically fit into the modular PSU port of another brand, the power delivery can be completely wrong, potentially causing damage.
- OEM Cables vs. Aftermarket: Even if you buy aftermarket cables that seem to fit, they may not be wired like the original cables supplied by your PSU manufacturer. This can lead to mismatches where the cable fits but doesn’t function properly.
3. Cable Misalignment or Damage:
Sometimes, the issue isn’t about the compatibility between the PSU and the motherboard but rather the cable’s condition or connection.
- 4+4-pin Misalignment: If your PSU has a 4+4-pin configuration, both halves of the cable need to fit into the motherboard’s CPU power socket. It’s easy to misalign them, especially when installing the cable in a cramped case. If the pins don’t perfectly line up, the cable may seem like it doesn’t fit.
- Damaged Connectors: Wear and tear, bent pins or frayed wires can cause a perfectly compatible cable to behave as if it doesn’t match. This is particularly common in older systems where the power cables have been through multiple installations or removals.
Diagnosing the Issue: Is Your PSU CPU Cable Mismatched?
Step 1: Check the Motherboard Manual
Start by consulting your motherboard’s manual to determine the CPU power connector required. You’ll typically find this information under the “Power Connector” or “CPU Power” section. Look for terms like “EPS,” “4-pin,” or “8-pin” to understand the power input requirements.
Step 2: Inspect Your PSU
Next, examine your PSU’s specifications to verify what kind of CPU power cables it provides. If you have a modular PSU, double-check that you’re using the correct cable for the CPU power slot. Most PSU manufacturers label their modular ports to prevent mixing up cables, but it’s always good to double-check.
Step 3: Test the Fit
If you suspect a cable misalignment, remove the CPU power cable and carefully reinstall it, ensuring that the pins are aligned correctly. With 4+4-pin connectors, getting both halves perfectly aligned in the socket can be tricky, especially in tight cases.
Step 4: Look for Damaged Components
Inspect the cable for any signs of damage, such as bent pins, worn-out connectors, or frayed wires. Even minor damage can prevent the cable from functioning correctly.
Future-Proofing Your PC Build

Check Power Requirements:
Before purchasing a PSU, check the power requirements of your CPU and motherboard. High-performance CPUs may require more power than a basic PSU can provide, so it’s essential to choose a unit with sufficient wattage and the correct connectors.
Look for Modular Flexibility:
While modular PSUs offer cleaner cable management, make sure that the modular cables are compatible with your build. Stick with the original cables provided by the manufacturer, or opt for modular PSUs with clearly labeled and easy-to-identify cable ports.
Consider Future Upgrades:
If you plan to upgrade your CPU or motherboard in the future, choose a PSU that provides a range of power connectors, including 4+4-pin and 8-pin options. This will give you flexibility when upgrading to more power-hungry components down the line.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Why doesn’t my 8-pin CPU connector match?
The 8-pin CPU connector may not match due to different connector types or incompatible cables. Verify your motherboard specs and use the correct PSU cable.
2. What is the EVGA CPU cable, and how does it work?
The EVGA CPU cable connects your power supply to the CPU power socket on the motherboard, providing essential power. It’s available in various configurations, like 4-pin or 8-pin.
3. What is the role of the CPU cable in connecting to the motherboard?
The CPU cable provides power from the power supply unit (PSU) to the CPU socket on the motherboard. It ensures the processor receives the necessary voltage for operation.
4. What is a PCIe cable, and what is its purpose in a computer system?
A PCIe cable is used to connect the power supply unit (PSU) to PCIe devices like graphics cards. It provides the necessary power for optimal performance and operation.
Conclusion:
If your PSU CPU cable is incompatible, verify whether you have a 4-pin or 8-pin connection or check for modular cable problems. Make sure you’re using the right cable, or think about upgrading your PSU.
Read Also: