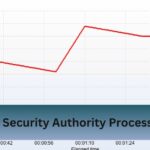
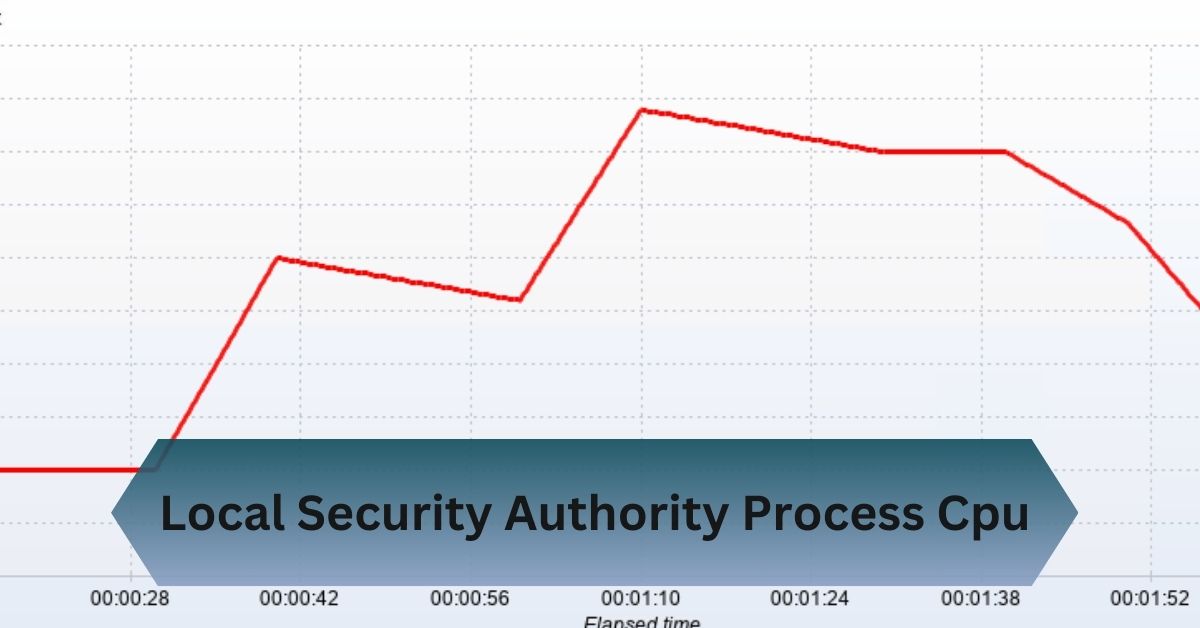
A few weeks ago, my laptop started running extremely slow, and I noticed LSASS.exe was using almost 50% of my CPU in Task Manager. After running a malware scan, I discovered a hidden trojan attempting to steal my credentials through LSASS.
The Local Security Authority Process (LSASS.exe) manages Windows authentication. High CPU usage may signal malware or system issues. Fix it by scanning for malware, updating Windows, and checking system logs.
Learn how to fix it and keep your system running smoothly!
Table of Contents
What is the Local Security Authority Process (LSASS)?
The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS), identified as lsass.exe, is an essential Windows process. It is responsible for handling crucial security-related tasks, including:
- User Authentication: Verifying usernames and passwords during the login process.
- Security Policy Management: Enforcing password changes, access control, and login rules.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Managing credential storage to allow users to access multiple resources without repeated logins.
- Encryption and Decryption: Protecting sensitive information and securing communications.
Role of LSASS in Windows Security
- Manages password changes and authentication for user accounts.
- Enforces security policies related to logins and access permissions.
- Handles Single Sign-On (SSO) for enterprise environments.
- Encrypts sensitive credentials to prevent unauthorized access.
Why LSASS is Important for System Integrity?
- Protects Windows authentication mechanisms.
- Prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data.
- Ensures compliance with security protocols in enterprise environments.
Read Also: Cpu Iphone Os 16 – Speed, Battery Life & Fixes!
Why is the Local Security Authority Process Using High CPU?
High CPU usage by the Local Security Authority Process can slow down your system and affect performance. Here are some common reasons:
1. System File Corruption:
When Windows system files are damaged or missing, LSASS may struggle to perform its tasks efficiently, leading to higher CPU consumption.
2. Malware Infection:
Malware or viruses often disguise themselves as lsass.exe to exploit system vulnerabilities. This can lead to abnormal CPU spikes.
3. Excessive Authentication Requests:
In corporate environments, domain controllers handle numerous authentication requests. A high volume can overload the LSASS process.
4. Windows Updates Issues:
Incomplete or failed updates can cause glitches, resulting in abnormal behavior of system processes, including LSASS.
5. Third-Party Software Conflicts:
Certain third-party applications interacting with system authentication can cause LSASS to consume excessive CPU resources.
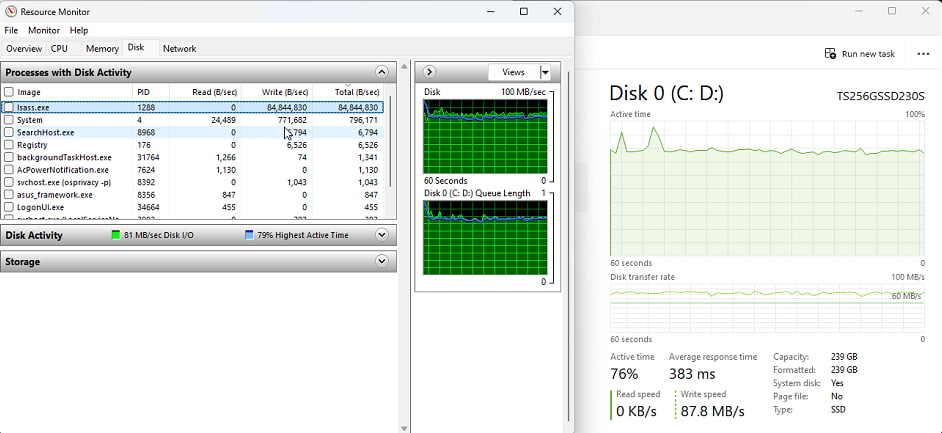
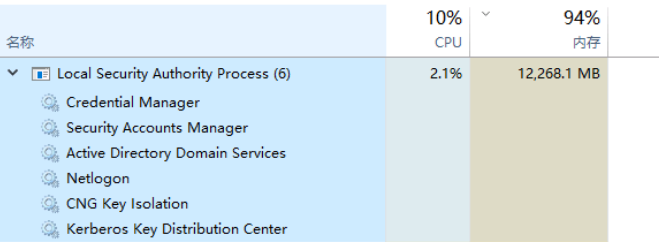
How to Check Local Security Authority Process CPU Usage?
Monitoring LSASS is simple with built-in Windows tools. Here’s how you can track its CPU consumption:
- Open Task Manager: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Locate LSASS.exe: Find Local Security Authority Process under the Processes tab.
- Check CPU Usage: Observe the CPU column to identify abnormal spikes.
How to Fix Local Security Authority Process High CPU Usage?
If you’re dealing with high CPU usage from LSASS, follow these troubleshooting steps:
Scan for Malware and Viruses:
Malware infections are a leading cause of LSASS CPU spikes. Use Windows Defender or a reputable third-party antivirus to detect and remove threats.
Steps to run a full scan:
- Open Windows Security from the Start menu.
- Select Virus & Threat Protection.
- Click Scan Options and choose Full Scan.
- Click Scan Now.
Check System Integrity with SFC and DISM:
Corrupted system files can trigger high LSASS usage. Use these commands to repair them:
Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
Run the following commands:
sfc /scannow
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
Update Windows:
Outdated systems may have bugs causing CPU spikes. Ensure you have the latest updates:
- Go to Settings > Windows Update.
- Click Check for Updates.
- Install any pending updates and reboot your system.
Analyze Event Viewer Logs:
Check Event Viewer for specific errors related to LSASS:
- Press Win + X and select Event Viewer.
- Navigate to Windows Logs > Security.
- Look for recurring errors and follow any suggested resolutions.
Stop Unnecessary Services:
Third-party services can cause conflicts with LSASS. Disable non-essential services to improve performance:
- Press Win + R, type msconfig, and hit Enter.
- Go to the Services tab and check Hide All Microsoft Services.
- Disable unnecessary services and reboot.
Read Also: Linux Distro For i686 Cpu – Revive Your Old Pc!
Managing Excessive Authentication Requests
High CPU usage in LSASS can be due to an overload of authentication requests, especially in enterprise environments with Active Directory.
Limiting Domain Authentication Overload:
- Check for repeated login failures that may indicate brute-force attempts.
- Reduce unnecessary domain authentication requests by setting up proper Group Policies.
- Limit expired session retries by adjusting Kerberos ticket expiration policies.
Investigating Network Login Failures:
- Open Event Viewer and check Security Logs for multiple failed login attempts.
- If using Active Directory, inspect domain controllers for excessive authentication requests.
Is the Local Security Authority Process Safe?
Yes, the genuine lsass.exe is a legitimate and vital Windows process. However, if you find it in a location other than C:\Windows\System32, it could be malicious.

How to Verify Authenticity:
- Right-click LSASS in Task Manager.
- Select Open File Location.
- Confirm the location is C:\Windows\System32.
If it is elsewhere, perform a thorough malware scan immediately.
When to Seek Professional Help:
If high Local Security Authority Process CPU usage persists despite following these steps, consider professional assistance. Persistent issues might indicate deeper system corruption or hardware malfunctions.
Signs you need expert help:
- Unresolved CPU spikes after troubleshooting.
- Frequent system crashes or blue screens.
- Suspicious processes alongside LSASS.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Can I disable LSASS.exe?
No, LSASS is a critical Windows process. Disabling it will cause the system to restart immediately, as it’s responsible for authentication and security enforcement.
2. What are the signs of LSASS-related malware?
- High CPU and memory usage.
- Unexpected system slowdowns.
- Repeated failed login attempts in Event Viewer.
- Unauthorized access or credential theft attempts.
3. How do I know if LSASS CPU usage is normal?
Normal LSASS CPU usage is usually below 5%. If it consistently spikes above 20-30% without active authentication processes, it may indicate an issue.
4. What happens if LSASS crashes?
If LSASS crashes, Windows will force a system reboot to prevent security vulnerabilities. A persistent LSASS crash may indicate malware or a system corruption issue.
5. Can third-party security tools help with LSASS issues?
Yes, security tools like Malwarebytes, Windows Defender, and Bitdefender can help detect malware affecting LSASS. However, some security software can also conflict with LSASS, so always ensure compatibility.
Conclusion:
LSASS.exe handles Windows authentication, but high CPU usage could mean malware or system problems. Resolve it by running a malware scan, updating Windows, and reviewing system logs for issues.
Read Also: