Upgrading a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) can significantly improve performance. However, many users wonder: Do I need a new motherboard for a new CPU?. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down everything you need to know to make an informed decision before upgrading.
A new motherboard is needed if the CPU socket, chipset, or BIOS isn’t compatible. Check your motherboard specs to ensure support or upgrade for full performance.
Make sure your motherboard can keep up for the best performance and compatibility!
Table of Contents
Understanding CPU and Motherboard Compatibility
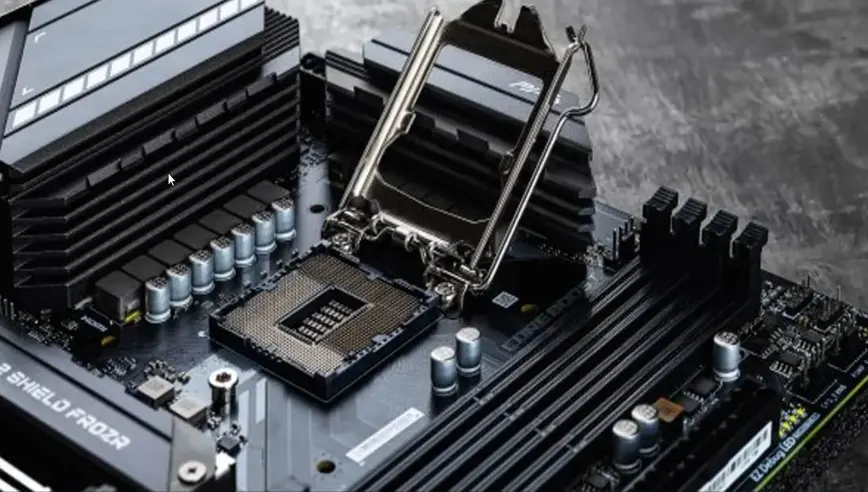
What is a CPU Socket, and Why Does It Matter?
A CPU socket is a specific slot on a motherboard where the processor is installed. Different CPUs are designed to fit only specific socket types. If your new CPU uses a different socket than your existing motherboard, you will need a new motherboard.
Common CPU Sockets:
- Intel: LGA1200, LGA1700, LGA1851
- AMD: AM4, AM5
For example, if you are upgrading from an Intel 10th-gen CPU (LGA1200) to a 14th-gen CPU (LGA1700), you must replace your motherboard since the sockets are different.
How Chipsets Affect Compatibility?
A chipset is the motherboard component that determines which CPUs, memory, and features the board supports. Even if your CPU physically fits into the socket, your motherboard’s chipset may not support it.
Example:
- Intel’s Z590 chipset supports 10th and 11th-gen Intel CPUs.
- Intel’s Z690 chipset supports 12th, 13th, and 14th-gen Intel CPUs with an LGA1700 socket.
- AMD’s X570 chipset supports Ryzen 3000 and 5000 series CPUs.
- AMD’s X670 chipset supports Ryzen 7000 series CPUs, but only on AM5 sockets.
Always check the chipset compatibility list on the manufacturer’s website before upgrading.
What Are the Benefits of Upgrading Your Motherboard?
If your new CPU requires a motherboard upgrade, you might gain several advantages:
- Better Power Delivery: High-performance CPUs require stable power delivery, which newer motherboards provide.
- More Expansion Slots: Support for more RAM, PCIe devices, and storage options.
- Future-Proofing: Modern motherboards support upcoming technologies like USB 4.0, PCIe 5.0, and WiFi 6.
- Improved Cooling and Performance Features: Advanced VRMs (Voltage Regulation Modules) and cooling solutions help sustain performance.
Do I Need a BIOS Update for a New CPU?
A BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is firmware that helps the motherboard communicate with the CPU and other components. Sometimes, motherboards can support newer CPUs with a BIOS update, eliminating the need for a new motherboard.
How to Check if a BIOS Update is Needed?
- Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website.
- Find your motherboard model.
- Check the CPU support list and BIOS version requirements.
- Update the BIOS if needed (follow manufacturer instructions carefully).
Warning: Updating the BIOS carries risks. A failed update can render the motherboard unusable, so proceed with caution.
Read Also: Photolibraryd High Cpu – Simple Solutions To Resolve It!
Will My RAM and Storage Work with a New CPU?
RAM Compatibility:
Newer CPUs often support advanced memory technologies. If your motherboard only supports DDR4 RAM but your new CPU requires DDR5, you will need a new motherboard that supports DDR5.
For example:
- Intel 12th, 13th, and 14th-gen CPUs support both DDR4 and DDR5, depending on the motherboard.
- AMD Ryzen 7000 series (AM5) exclusively supports DDR5 RAM.
Storage Considerations:
Most modern motherboards support SSDs and NVMe drives, but newer chipsets offer PCIe Gen 4 or Gen 5 support for faster speeds. If you plan to upgrade to a high-speed SSD, ensure your new motherboard supports the necessary PCIe generation.
When You Don’t Need a New Motherboard?
If your existing motherboard supports your new CPU’s socket, chipset, and BIOS version, then an upgrade is unnecessary. However, ensure it provides adequate power delivery and RAM support.

Upgrades That Don’t Require a New Motherboard:
- Upgrading from Intel 12th-gen to 13th-gen (both use LGA1700 and similar chipsets).
- Upgrading from Ryzen 3000 to Ryzen 5000 on an AM4 motherboard with a BIOS update.
When You Must Get a New Motherboard?
If your new CPU uses a different socket or requires features your motherboard doesn’t support, you’ll need a new motherboard. This includes:
- Switching from Intel to AMD or vice versa.
- Upgrading from AM4 to AM5 (Ryzen 7000 series).
- Moving from LGA1200 to LGA1700 (Intel 11th-gen to 12th-gen+).
Read Also: Print Filter Pipeline Host High Cpu – Try These Fixes Now!
Potential Challenges When Upgrading a Motherboard
1. Windows Reinstallation May Be Required:
Changing the motherboard can cause activation issues with Windows. You might need to reactivate your OS or reinstall Windows completely.
2. Driver Compatibility Issues:
A new motherboard may require different drivers for Ethernet, audio, and other components.
3. Form Factor Considerations:
Ensure your new motherboard fits your PC case. Common form factors include:
- ATX (standard).
- Micro-ATX (smaller).
- Mini-ITX (compact).
How to Choose the Right Motherboard for Your New CPU?
If you need a new motherboard, consider these factors:

- CPU Compatibility – Ensure the socket and chipset match your CPU.
- Memory Support – DDR4 or DDR5 compatibility.
- Expansion Slots – PCIe lanes for GPUs, SSDs, and other peripherals.
- Connectivity – USB-C, Thunderbolt, WiFi 6, Bluetooth support.
- Overclocking Support – If you plan to overclock, choose a motherboard with strong VRMs.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Will a new motherboard improve gaming performance with the same CPU?
A high-end motherboard can enhance performance by offering better power delivery, faster RAM support, and improved PCIe lanes for GPUs and SSDs.
2. Do I need a new motherboard if switching from Intel to AMD or vice versa?
Yes, Intel and AMD use completely different sockets and chipsets, making a motherboard change necessary when switching between the two brands.
3. Can a motherboard bottleneck a new CPU’s performance?
Yes, a low-end motherboard with weak VRMs or outdated features can limit your CPU’s potential, causing throttling or reduced overclocking capabilities.
4. How do I check if my motherboard supports a new CPU?
Visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website, check the CPU compatibility list, and ensure your BIOS version supports the new processor.
Conclusion:
A new motherboard is required if your new CPU isn’t compatible with the existing socket, chipset, or BIOS. Even if a BIOS update allows partial support, older motherboards may limit performance, power efficiency, and features. Always check your motherboard specifications to ensure full compatibility or upgrade for better stability, speed, and future-proofing.
Related Posts: