When it comes to pushing your CPU to its maximum potential, ensuring stable voltage delivery is paramount. This is where CPU Vcore Loadline Calibration (LLC) plays a critical role.
CPU Vcore Loadline Calibration stabilizes voltage, reduces Vdroop, ensures performance stability, and is vital for safe overclocking and preventing hardware damage.
Stabilize voltage, boost performance, and ensure safe overclocking like a pro!
Table of Contents
What is CPU Vcore?
CPU Vcore, or core voltage, refers to the amount of electrical power supplied to your CPU’s cores. It is a critical factor in maintaining stable performance, especially under load.
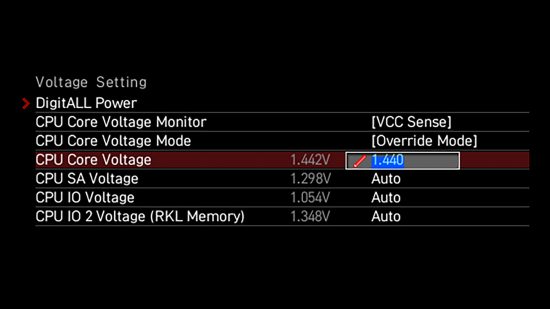
Insufficient Vcore can cause system instability, while excessive Vcore can lead to overheating and hardware damage. Striking the right balance is key, and this is where loadline calibration steps in.
What is Loadline Calibration (LLC)?
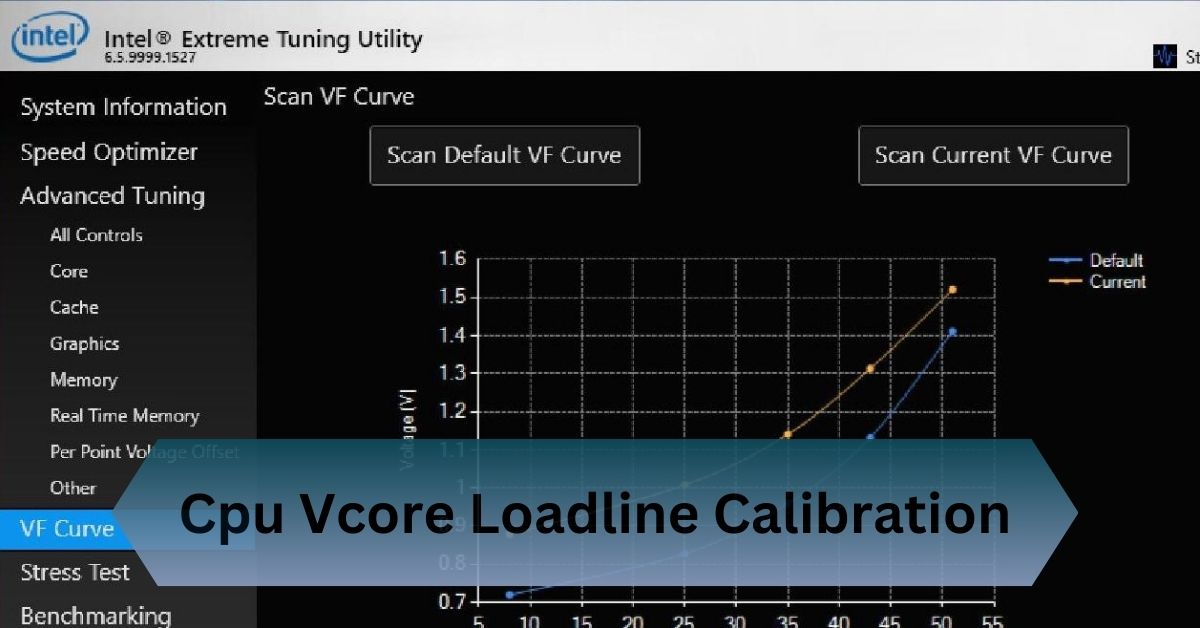
Loadline Calibration (LLC) is a motherboard feature designed to stabilize CPU voltage delivery. When your CPU transitions from idle to load states, the voltage supplied by the motherboard can fluctuate due to resistance in the power delivery system. LLC minimizes these fluctuations, ensuring consistent voltage levels and preventing Vdroop.
Why is Loadline Calibration Important?
Without proper voltage regulation, CPUs can experience instability during heavy workloads or overclocking. LLC acts as a safeguard, reducing voltage dips (Vdroop) that occur when the CPU demands more power.
This helps maintain system stability and enhances performance, especially during overclocking.
Read Also: What Is Cpu Cycle – How Your Computer Works!
How Does Loadline Calibration Work?
- Idle State: When the CPU is idle, the power demand is low, and the Vcore remains stable without much adjustment.
- Load Transition: As the CPU transitions to a high-load state, the sudden demand for power causes a drop in Vcore (Vdroop).
- Compensation: LLC detects this drop and increases the Vcore slightly to counteract the Vdroop.
- Stable Operation: With the adjusted Vcore, the CPU continues operating stably even under heavy workloads.
Understanding LLC Levels
Most modern motherboards offer multiple levels of LLC, allowing users to fine-tune the compensation for Vdroop.
- Level 1 (Aggressive): Provides the highest compensation for Vdroop, resulting in minimal voltage drop but potentially causing overvoltage.
- Level 2-4 (Moderate): Offers balanced compensation, suitable for most users and workloads.
- Level 5+ (Minimal): Keeps compensation minimal, allowing for slight Vdroop and prioritizing safety over performance.
Choosing the right LLC level depends on your specific needs and hardware configuration. For overclocking, higher levels are often preferred to maintain stability at higher CPU frequencies. For stock settings, moderate levels are usually sufficient.
Benefits of Proper Loadline Calibration

Stability During Overclocking:
One of the primary benefits of LLC is enhanced stability during overclocking. By maintaining consistent voltage levels, LLC allows you to push your CPU further without encountering crashes or instability.
Improved System Longevity:
Fluctuating voltages can stress your CPU and motherboard components, potentially shortening their lifespan. Proper LLC configuration reduces this stress, contributing to longer-lasting hardware.
Consistent Performance Under Load:
With stable voltage delivery, your CPU can perform consistently even under heavy workloads. This is particularly beneficial for gamers, content creators, and professionals who rely on steady performance.
How to Configure Loadline Calibration?
Enter BIOS/UEFI:
Restart your computer and press the designated key (usually Delete or F2) during startup to enter the BIOS/UEFI menu.
Locate LLC Settings:
Navigate to the Advanced Settings or Overclocking section. Look for options related to CPU Vcore or Loadline Calibration.
Select LLC Level:
Choose an LLC level based on your requirements. Start with a moderate level and adjust as needed based on system stability and performance.
Save and Exit:
Save your changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI. Your system will reboot with the new settings.
Test Stability:
Use stress-testing tools like Prime95 or AIDA64 to ensure your system remains stable under load.
Read Also: I/O Bound Vs Cpu Bound – Boost Your System’s Efficiency Today!
Potential Risks of Misconfiguring Loadline Calibration

Voltage Overshoot:
While LLC is designed to counteract Vdroop, overly aggressive settings can lead to voltage overshoot, where the CPU receives more voltage than intended. This can cause overheating and damage sensitive components.
Increased Power Consumption:
Higher LLC levels often result in increased power draw, which can lead to higher electricity bills and greater heat output. Balancing performance and efficiency is crucial.
Hardware Damage Risks:
Improper LLC configuration can lead to excessive voltage levels, posing a risk to your CPU and motherboard. Always test and monitor your settings to avoid potential damage.
Loadline Calibration and Overclocking
Importance of LLC in Overclocking Scenarios:
Overclocking increases your CPU’s frequency, requiring higher and more stable voltage levels. Without LLC, Vdroop during high loads can cause instability, leading to crashes or throttling. LLC ensures the CPU receives consistent voltage, making it a crucial component of any overclocking strategy.
Fine-Tuning LLC Settings for Stable Overclocks:
Achieving a stable overclock involves fine-tuning both the CPU multiplier and LLC levels. Start with moderate LLC settings and gradually increase the multiplier. Use stress-testing tools to identify the point at which your system remains stable. If you notice voltage drops or instability, consider raising the LLC level incrementally.
Avoiding Common Mistakes During Overclocking:
Many beginners make the mistake of setting LLC to the highest level, thinking it will guarantee stability. However, this can lead to voltage overshoot, overheating, and long-term hardware damage. Always balance LLC settings with other parameters like core voltage and temperature limits.
Tips for Safe and Effective Loadline Calibration

Gradual Adjustments to LLC Levels:
When tweaking LLC, always make incremental adjustments. Jumping to the highest level immediately can lead to instability or hardware damage. Start with moderate settings and test thoroughly before making further changes.
Monitoring Temperature and Power Draw:
LLC adjustments can affect your CPU’s power draw and temperature. Keep an eye on these factors using monitoring tools to ensure your cooling system can handle the additional load.
Seeking Expert Advice When Needed:
If you’re unsure about LLC settings, consult your motherboard’s manual or online forums for guidance. Many overclocking communities have experienced users who can offer tips specific to your hardware.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the ideal LLC level for overclocking?
The ideal LLC level depends on your CPU and motherboard. Start with moderate levels (e.g., Level 3 or 4) and adjust based on stability and voltage monitoring results.
2. Can incorrect LLC settings damage the CPU?
Yes, overly aggressive LLC settings can cause voltage overshoot, which may damage the CPU and other components over time.
3. Is loadline calibration necessary for non-overclocked systems?
For non-overclocked systems, default LLC settings are usually sufficient. However, fine-tuning LLC can still improve stability in specific scenarios.
4. How does LLC affect CPU temperature?
Higher LLC levels can increase CPU temperature due to higher voltage delivery. Always monitor your temperatures and ensure adequate cooling.
Conclusion:
CPU Vcore Loadline Calibration reduces Vdroop, stabilizes voltage, enhances performance reliability, and is essential for safe overclocking and protecting hardware.
Related Posts: