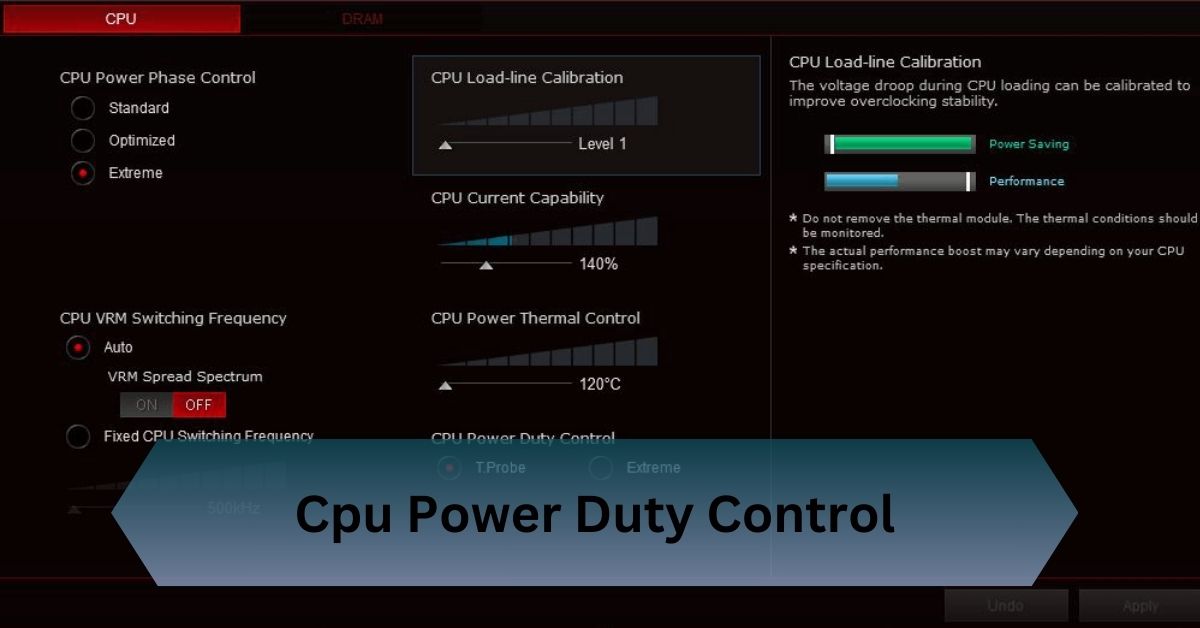
When I first delved into overclocking my PC, I was amazed at how much CPU Power Duty Control influenced my system’s stability. By fine-tuning the power phases and voltage settings, I achieved a smoother performance boost without crashing.
CPU Power Duty Control optimizes power delivery to your CPU, enhancing stability and performance. By adjusting power phases and voltage settings, users can achieve better overclocking results and improve energy efficiency. Proper configuration ensures a balance between power, heat, and system reliability.
Discover how CPU Power Duty Control can transform your PC’s performance and efficiency with just a few tweaks in your BIOS settings!
Table of Contents
Understanding CPU Power Duty Control
CPU Power Duty Control is a feature in your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings that helps manage how power is delivered to your CPU. It adjusts the way power phases and voltage are handled to ensure that the CPU gets the right amount of power under different conditions.
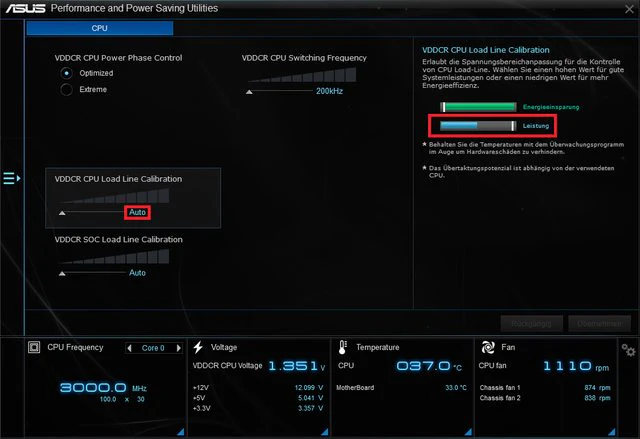
This helps in maintaining stable performance, especially if you’re overclocking your CPU for better speed or aiming for energy efficiency. By fine-tuning these settings, you can enhance your system’s stability and potentially save on power consumption.
Basics of Power Delivery
To grasp the concept of CPU Power Duty Control, it’s important to understand the basics of power delivery to the CPU. Modern CPUs are complex components that require a stable and efficient power supply to operate correctly.
Power delivery involves converting the power from your PSU (Power Supply Unit) into a form that the CPU can use. This process is managed by the motherboard’s power regulation circuitry, which often includes phases and voltage regulators.
The Role of Duty Control
Duty control, in the context of power delivery, refers to the regulation of power phases and the timing of power delivery to the CPU. By adjusting duty control settings, you can influence how power is supplied under different load conditions. This is where CPU Power Duty Control comes into play.
Why Does CPU Power Duty Control Matter?
- Steady Power Supply: Ensures the CPU receives a consistent and adequate power supply.
- Improves Stability: Reduces the risk of system crashes and freezes, especially during high-demand tasks or overclocking.
- Prevents Performance Issues: Helps avoid performance problems caused by inconsistent power delivery.
- Optimizes Power Phases: Manages power phases and voltage settings to maintain stability and reliability.
- Enhances Reliability: Contributes to a more stable and dependable computing experience by fine-tuning power delivery.
Key Features of CPU Power Duty Control
Power Phases Management:
One of the primary aspects of CPU Power Duty Control is managing power phases. Power phases are segments of the power delivery system responsible for providing the CPU with stable power. More phases typically mean better power regulation and stability, especially under high loads. CPU Power Duty Control settings allow users to adjust how these phases operate, which can impact overall system stability and performance.
Voltage Regulation:
Another critical feature is voltage regulation. Proper voltage levels are crucial for CPU stability and performance. CPU Power Duty Control lets users fine-tune voltage settings to ensure that the CPU receives the correct amount of power, enhancing stability and potentially improving overclocking results.
Duty Cycle Adjustments:
Duty cycle adjustments refer to the balance of power delivery over time. By configuring these settings, users can influence how the CPU handles power under varying workloads, affecting both performance and power efficiency.
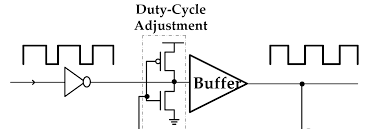
The Role of CPU Power Duty Control
Balancing Power Distribution:
CPU Power Phase Control balances how power is distributed across different phases, helping to smooth out fluctuations and deliver consistent power to the CPU. This balance is critical for maintaining performance during varying workloads.
Reducing Heat Generation:
By optimizing power delivery, CPU Power Phase Control helps manage heat output. Efficient power distribution means less excess heat, which helps in keeping the CPU cooler and prolongs the lifespan of the components.
Enhancing Component Longevity:
Stable power delivery and efficient management of power phases contribute to the longevity of both the CPU and the motherboard. Proper control reduces wear and tear on components, leading to a more durable system.
Adapting to Workload Changes:
This feature allows the system to adapt to different workload requirements by adjusting power phases dynamically. It ensures that the CPU gets the appropriate amount of power based on its current demands, enhancing performance and efficiency.
Practical Tips for Effective Use
1. Start with Default Settings:
If you’re new to configuring CPU Power Duty Control, start with the default settings provided by your motherboard manufacturer. This ensures that you have a stable baseline from which to make adjustments.
2. Incremental Changes:
Make incremental adjustments to avoid destabilizing your system. Adjust one setting at a time and test system stability before making further changes.
3. Monitor and Test:
Use monitoring software to keep an eye on system temperatures, voltages, and performance. Stress test your system to ensure that it remains stable under load after making adjustments.
4. Seek Expert Advice:
If you’re unsure about how to configure CPU Power Duty Control settings, seek advice from experienced users or consult your motherboard’s documentation. Online forums and communities can also provide valuable insights.
What are duty cycles in CPU Power Duty Control?
Duty cycles in CPU Power Duty Control refers to how power is delivered to your CPU over time. Imagine it as the timing of when your CPU gets power and when it doesn’t.
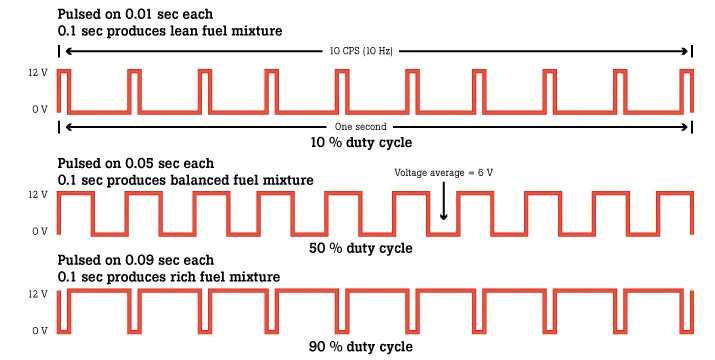
A well-adjusted duty cycle ensures that the CPU receives the right amount of power exactly when needed, which is especially important during demanding tasks like gaming or video editing.
By properly managing duty cycles, your system can run more smoothly, avoiding power issues that might cause crashes or slowdowns.
It also helps in saving energy by not delivering too much power when it’s not necessary, keeping your system cooler and more efficient. In short, duty cycles are all about making sure your CPU gets the power it needs, just when it needs it.
Overheating from Improper Power Duty Control
- Inconsistent Power Delivery: Incorrect settings can lead to an unstable power supply, causing the CPU to work harder than necessary, and generating excess heat.
- Increased Voltage: If voltage settings are too high, the CPU may draw more power than needed, leading to higher temperatures and potential overheating.
- Lack of Cooling: Improper power settings can outpace your cooling system’s ability to manage heat, resulting in overheating.
- System Instability: Overheating from poor power control can cause system crashes, reduced performance, and long-term damage to components.
- Reduced Component Lifespan: Persistent overheating can degrade the CPU and other components faster, shortening their overall lifespan.
FAQs:
1. What is CPU Power Phase Control Extreme?
CPU Power Phase Control Extreme activates all power phases to enhance stability and performance, especially during heavy tasks or overclocking. It ensures consistent power delivery, minimizing the risk of instability and overheating.
2. What Does CPU VRM Thermal Control Do?
CPU VRM Thermal Control keeps the Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) cool, preventing overheating and ensuring stable power delivery to the CPU. This feature helps maintain system reliability during intense workloads.
3. Should CPU VRM Thermal Control be enabled or disabled?
CPU VRM Thermal Control should generally be enabled to ensure the VRM stays cool and maintains stable power delivery. Disabling it can risk overheating and instability during high-performance tasks.
4. How do I control my CPU power?
Control CPU power via BIOS/UEFI settings by adjusting power management and voltage settings. Software tools for your motherboard can also help fine-tune power delivery.
Conclusion:
CPU Power Duty Control enhances CPU stability and performance by optimizing power delivery. Adjusting power phases and voltage settings can improve overclocking results and boost energy efficiency, ensuring a balance between power, heat, and system reliability.