When you power on your computer, a series of intricate processes take place behind the scenes before you see the operating system’s splash screen. One of these crucial processes is CPU POST (Power-On Self-Test) Memory Initialization.
CPU POST Memory Initialization is a crucial startup phase where the CPU checks, tests, and configures RAM to ensure it’s functioning correctly before the OS loads.
“Ever wondered how your CPU breathes life into your system’s memory? Discover the magic of CPU post memory initialization!”
Table of Contents
What is POST?
POST, or Power-On Self-Test, is the initial diagnostic process when you turn on your computer. It’s a series of checks and tests conducted by the computer’s motherboard to ensure that all essential hardware components are operational before the system starts loading the operating system.
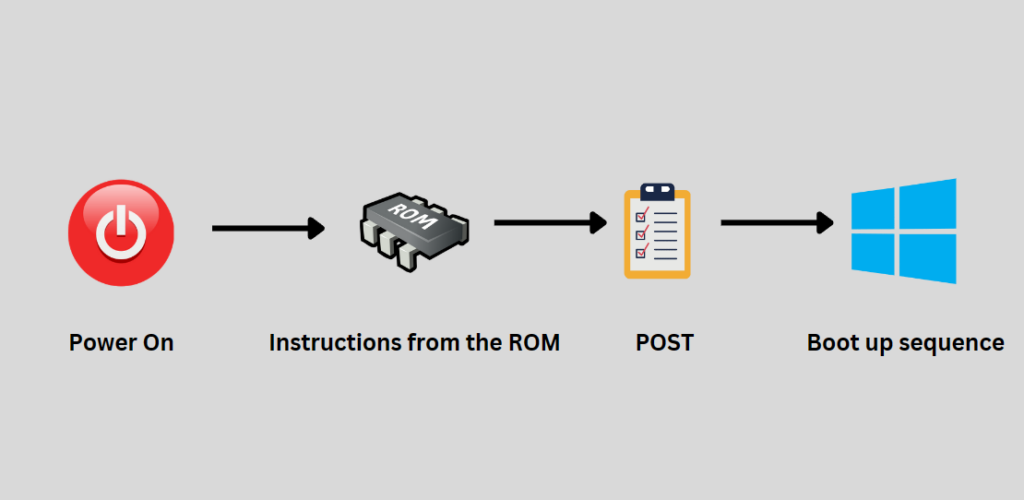
Think of POST as the computer’s saying, “Let me check if everything is in order before we get started.”
The Role of Memory Initialization in POST
One of the critical tasks during the POST process is Memory Initialization. Memory Initialization involves the CPU (Central Processing Unit) verifying and setting up the computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory).
RAM is a type of volatile memory that the CPU uses to store data currently being used or processed. Without properly initialized memory, your computer cannot perform tasks effectively.
The Crucial Role of Pre-Memory CPU Initialization
- Initial Check: It’s the CPU’s way of checking that everything is set up correctly before the computer starts running. This includes making sure the RAM (memory) is working and properly connected.
- Ensures Stability: Verifying and configuring memory at the start helps prevent crashes and system errors later, making your computer more stable and reliable.
- Performance Boost: Proper initialization ensures that the RAM is set up to work efficiently, which can help your computer run faster and handle more tasks simultaneously.
- Error Detection: If there’s a problem with the RAM or other components, pre-memory initialization can catch these issues early. This allows you to fix problems before they cause bigger issues.
- Smooth Startup: The computer can load the operating system smoothly and quickly by getting the memory ready and confirming everything is in order.
Why Pre-Memory CPU Initialization Error Occurs?
- Faulty RAM: Defective or improperly seated memory modules can prevent the CPU from initializing the memory, leading to errors.
- Motherboard Issues: Problems with the motherboard, such as damaged components or poor connections, can disrupt the initialization process.
- Power Supply Problems: An inadequate or failing power supply can cause insufficient power delivery, affecting the CPU’s ability to initialize memory.
- CPU Problems: A malfunctioning or improperly installed CPU can prevent successful memory initialization.
- BIOS/UEFI Issues: Outdated or corrupt BIOS/UEFI firmware can cause errors during the initialization process.
- Hardware Incompatibility: Incompatibilities between the CPU, RAM, and motherboard can lead to initialization errors.
- Loose Connections: Loose or disconnected cables and components can interfere with initialization.
- Thermal Issues: Overheating due to inadequate cooling can affect the CPU and memory, leading to errors during initialization.
- Electrical Faults: Electrical issues, such as short circuits or static discharge, can disrupt the initialization process.
Read Also: Cpu Privileged Time Is Too High Zabbix – Lower It’s Time Today!
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While POST Memory Initialization is a crucial process, it can sometimes encounter issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
Memory Errors:
If the CPU detects faulty memory, it may produce beep codes or error messages. These codes can help identify the problem, such as a defective RAM module or improper installation.
No POST:
If the system does not complete POST, it could be due to various reasons, including faulty RAM, motherboard issues, or power supply problems. Check all connections and ensure that the RAM modules are properly seated.
System Instability:
If your computer experiences random crashes or freezes after POST, it may be due to improperly configured memory settings. Check the BIOS settings and ensure that memory timings and voltages are set correctly.
Beep Codes:
Many motherboards have built-in speakers that produce beep codes during POST. Refer to your motherboard’s manual to decode these beeps and identify potential issues.
Solutions Of Pre-Memory Cpu Initialization Error
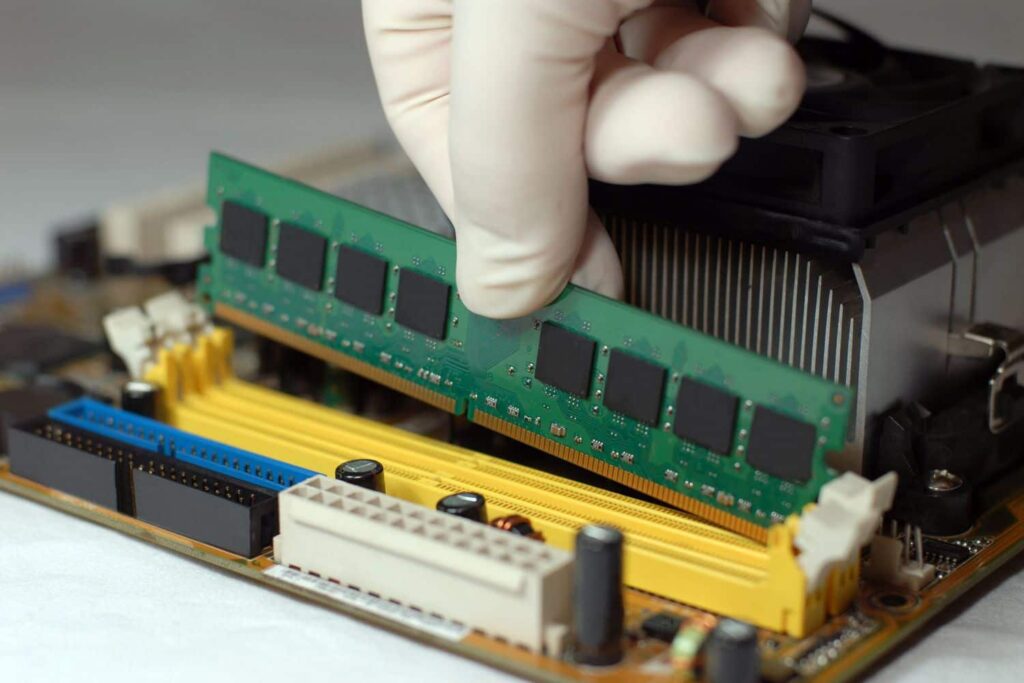
Check RAM Modules:
- Reseat RAM: Ensure memory modules are properly seated in their slots.
- Test RAM: Use a memory diagnostic tool or swap RAM modules to identify faulty memory.
- Try Different Slots: Test RAM in different slots to rule out slot issues.
Inspect the Motherboard:
- Check for Damage: Look for visible signs of damage or loose components.
- Reseat Components: Ensure all components, including the CPU and expansion cards, are securely installed.
- Examine Connections: Verify that all power cables and internal connections are properly connected.
Power Supply Check:
- Verify Power Supply: Ensure the power supply provides adequate power and is functioning correctly.
- Check Cables: Confirm that all power cables are securely connected to the motherboard and components.
CPU Examination:
- Reseat CPU: Carefully remove and reinstall the CPU, ensuring it is properly aligned and seated.
- Inspect for Damage: Check the CPU for any physical damage or bent pins.
Update or Reset BIOS/UEFI:
- Update Firmware: Download and install the latest BIOS/UEFI firmware from the motherboard manufacturer’s website.
- Reset Settings: Use the motherboard’s jumper or battery removal method to reset BIOS/UEFI settings to default.
Verify Hardware Compatibility:
- Verify Compatibility: Ensure that the CPU, RAM, and motherboard are compatible.
- Consult Documentation: Review the motherboard’s manual for compatibility information and installation guidelines.
Verify Connections:
- Inspect Cables: Ensure all internal and external cables are connected and undamaged.
- Check Power Button: Confirm that the power button and front panel connections are correctly attached.
Address Thermal Issues:
- Check Cooling System: Ensure the CPU cooler and fans are properly installed and functioning.
- Clean Dust: Remove any dust buildup that could affect cooling.
Test for Electrical Faults:
- Inspect for Shorts: Check for signs of short circuits or static discharge that might have affected the components.
- Use a Surge Protector: Connect your computer to a surge protector to prevent electrical issues.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How do I free up CPU memory?
To free up CPU memory, close unused applications and background processes to reduce memory usage. Additionally, you can increase virtual memory or upgrade your RAM for better performance.
2. What should memory be in Task Manager?
In Task Manager, memory usage should ideally be within the limits of your installed RAM, with some buffer for smooth performance. If memory usage is consistently high or close to 100%, it may indicate that you need to close applications or upgrade your RAM.
3. What does a CPU POST memory initialization error 36 mean?
A CPU POST memory initialization error 36 usually points to issues with the RAM or motherboard. Reseating memory and checking connections can help resolve it.
4. How does CPU POST memory initialization affect Windows 11?
CPU POST memory initialization ensures that RAM is properly checked and configured before Windows 11 loads. This process helps prevent memory-related issues and ensures a stable system startup.
5. How does CPU POST memory initialization impact system performance?
Proper CPU POST memory initialization ensures that RAM is correctly configured, which is crucial for optimal system performance. Errors during this phase can lead to instability and reduced performance.
Conclusion:
CPU POST Memory Initialization is a vital step when you start your computer. During this phase, the CPU checks and sets up the RAM to ensure it works properly before the operating system begins to load. This process ensures the computer’s memory is ready for smooth and stable performance.
Read Also: