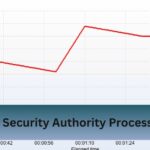
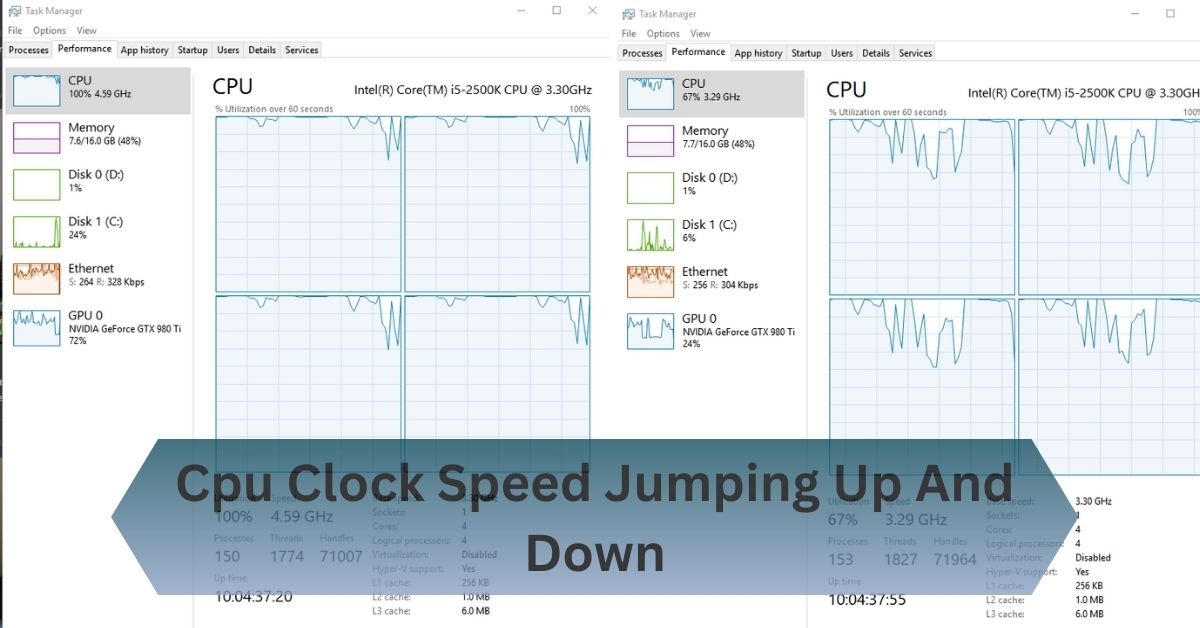
I noticed my laptop’s performance was inconsistent during gaming sessions, with the CPU clock speed jumping up and down. This caused sudden slowdowns and stutters, disrupting my gameplay.
Experiencing CPU clock speed jumping up and down can indicate issues like thermal throttling, power management settings, or background processes. To address this, check your cooling system, adjust BIOS settings, and monitor power supply stability. Proper troubleshooting can help stabilize performance and ensure smoother operation.
Let’s Start the process of cooling and optimizing with us.
Table of Contents
What is CPU Clock Speed?
Before we dive into the fluctuations, let’s start with the basics. CPU clock speed, expressed in gigahertz (GHz), indicates the number of cycles a CPU can perform each second.

Higher clock speeds generally mean that the CPU can process more instructions per second, leading to faster performance. For instance, a CPU with a clock speed of 4 GHz can handle 4 billion cycles per second.
Symptoms Of Cpu Clock Speed Fluctuations:
- Inconsistent Performance: Noticeable variations in system speed, with periods of lag or sudden drops in performance during tasks that require steady CPU power.
- System Slowdowns: Sluggish behavior in applications or delays in executing commands, especially during intensive tasks like gaming or video editing.
- Frequent Stutters or Freezes: Occasional stuttering or freezing of the system, which can be particularly noticeable during resource-heavy activities.
- Increased Fan Noise: Louder-than-usual fan noise as the system attempts to cool down the CPU due to overheating.
- Unexpected Shutdowns or Restarts: Random system crashes, shutdowns, or restarts may occur if the CPU temperature becomes too high or if power delivery is unstable.
- High-Temperature Readings: Elevated temperature readings from monitoring tools, indicate that the CPU is operating at higher temperatures than normal.
- Reduced Battery Life (Laptops): Decreased battery life in laptops, as fluctuating clock speeds can lead to inefficient power management.
Why Does CPU Clock Speed Fluctuate?
Thermal Throttling:
When a CPU gets too hot, it reduces its clock speed to prevent overheating. This process, known as thermal throttling, helps protect the hardware but can cause noticeable fluctuations in performance.
Power Management Features:
Modern CPUs use dynamic frequency scaling and power management technologies to adjust clock speeds based on current workload and power consumption. Features like Intel’s Turbo Boost and AMD’s Precision Boost automatically increase or decrease speed to balance performance and energy efficiency.
Background Processes:
Background applications and system tasks can intermittently demand more CPU resources, leading to temporary increases in clock speed. As these tasks start and stop, you may observe fluctuations in the CPU’s operating frequency.
Power Supply Issues:
An unstable or inadequate power supply can cause erratic CPU performance, including fluctuations in clock speed. Consistent power delivery is essential for maintaining stable CPU operation.
BIOS/UEFI Settings:
Settings in the BIOS or UEFI firmware can influence CPU clock speeds. Power-saving modes or overclocking settings may cause the CPU to vary its clock speed based on configured parameters or system needs.
How Does Thermal Throttling Affect CPU Clock Speed?
- Overheating Detection: When a CPU temperature exceeds a certain threshold, thermal throttling activates to protect the processor from damage.
- Clock Speed Reduction: To lower its temperature, the CPU reduces its clock speed. This means it processes fewer cycles per second, resulting in decreased performance.
- Performance Impact: As the clock speed drops, the CPU handles fewer instructions, leading to slower processing times. This can cause noticeable lag or reduced responsiveness in demanding applications.
Ways to Optimize CPU Clock Speed:
1. Improve Cooling:
Enhancing your CPU cooling system can prevent overheating and reduce thermal throttling. Consider using high-quality thermal paste, upgrading your heatsink, or adding additional case fans to improve airflow.

2. Adjust BIOS/UEFI Settings:
Access your BIOS or UEFI settings to optimize CPU performance. Disable unnecessary power-saving features, enable performance modes, and adjust settings related to overclocking if supported.
3. Monitor and Manage Background Processes:
Keep an eye on background applications that may be using CPU resources. Use tools like Task Manager or Activity Monitor to identify and manage processes that impact CPU performance.
4. Ensure Stable Power Supply:
A stable and adequate power supply is crucial for consistent CPU performance. Check that your PSU provides enough wattage and stable voltage for your system.
5. Update Drivers and Firmware:
Ensure that your system drivers and BIOS/UEFI firmware are up to date. Updates can improve system stability and performance, potentially affecting CPU clock speed optimization.
6. Overclocking (Optional):
For advanced users, overclocking can increase CPU clock speeds beyond default settings. Use reliable overclocking tools and monitor temperatures closely to avoid overheating.
7. Regular Maintenance:
Perform regular system maintenance, including cleaning dust from cooling components and checking for any hardware issues that could affect CPU performance.
How Does Clock Speed Impact Gaming Performance?
- Faster Processing: Higher clock speeds mean the CPU can handle more calculations per second, leading to smoother gameplay and faster response times.
- Better Frame Rates: With a faster clock speed, games can run at higher frame rates, providing a more fluid and enjoyable visual experience.
- Improved Responsiveness: A higher clock speed helps reduce lag and input delay, making your controls feel more immediate and precise.
- Enhanced Performance in Demanding Games: For resource-intensive games, a higher clock speed can help maintain performance and avoid slowdowns.
How Much Clock Speed Is Best For Cpu?
The best clock speed for a CPU depends on what you use your computer for. For everyday tasks like web browsing and office work, a clock speed between 3.0 GHz and 4.0 GHz is usually enough.
If you’re into gaming or using your computer for demanding tasks like video editing, a higher clock speed of 4.0 GHz to 5.0 GHz or more can offer better performance. Keep in mind that clock speed is important, but other factors like the number of CPU cores and overall design also matter.
FAQs:
1. Why is my CPU clock speed changing?
Your CPU clock speed might be changing due to thermal throttling, power management settings, or varying workload demands. These factors adjust the speed to manage heat, energy use, and performance efficiently.
2. Should the CPU clock fluctuate?
Yes, it’s normal for CPU clock speed to fluctuate as it adjusts to varying workloads and power management needs. This helps balance performance and energy efficiency.
3. Why is my CPU clock speed stuck?
Your CPU clock speed might be stuck due to issues like thermal throttling, power supply problems, or incorrect BIOS/UEFI settings. Ensuring proper cooling and checking settings can help resolve this.
4. Can a software update affect CPU clock speed?
Yes, software updates, particularly those related to system drivers or BIOS/UEFI firmware, can impact CPU clock speed by introducing changes in power management, performance settings, or system stability.
5. How does enabling CPU overclocking affect clock speed stability?
Enabling CPU overclocking increases the clock speed beyond default settings, which can lead to greater performance but may also cause instability if cooling and power supply are not adequate. Properly configuring overclocking settings and ensuring adequate cooling is crucial for maintaining stability.
Conclusion:
If your CPU clock speed is fluctuating, it could be due to thermal throttling, power management settings, or active background processes. To fix this, inspect your cooling system, adjust BIOS settings, and check your power supply. Effective troubleshooting can stabilize performance and improve overall system smoothness.