I once ran Cinebench on my overclocked CPU without checking temperatures, and my system overheated, forcing a shutdown. Luckily, no permanent damage occurred, but it reminded me how crucial good cooling is. Since then, I have constantly monitored temperatures while benchmarking to avoid risks.
Cinebench won’t damage your CPU, but overheating can occur without proper cooling. Monitor temps and ensure good airflow to benchmark your system safely.
Cinebench pushes your CPU to the max, but with proper cooling and temperature monitoring, you can safely unleash your system’s full potential!
Table of Contents
What Is Cinebench?
Cinebench, developed by Maxon, is benchmarking software designed to test your CPU’s performance. It simulates heavy-duty tasks like rendering 3D scenes, giving you a score based on how well your processor handles these tasks.
- Multi-threaded Test: Cinebench pushes all CPU cores to work together, simulating tasks requiring much power.
- Single-threaded Test: Cinebench tests how well your CPU handles tasks using only one core, which is important for software that doesn’t use multiple cores.
Can Stress Tests Like Cinebench Harm Your CPU?
Stress tests like Cinebench put your CPU through its paces, but they differ significantly from how you’d typically use your computer day-to-day.
When running Cinebench, your CPU is pushed to 100% load, which is rare unless you do demanding tasks like 3D rendering or video encoding.
Although stress testing doesn’t usually damage the CPU, repeatedly pushing it to its maximum performance without proper cooling can increase wear and tear. It’s akin to driving a car at top speed for hours – while the car can handle it, it’s not how it’s meant to operate all the time.
Read Also: Logonui.Exe High CPU – Effective Fixes And Prevention Tips!
When Could Cinebench Cause Issues?
While Cinebench is generally safe, there are certain scenarios where it could cause problems:
1. Poor Cooling or Dust Buildup:
If your computer isn’t well-cooled or if your fans are clogged with dust, running Cinebench could cause your CPU to overheat. This is especially true in older systems that haven’t been cleaned. Regularly clean dust from your PC and ensure good airflow inside your case.
2. Older Systems:
Older CPUs may struggle to handle the intense workloads Cinebench applies, especially if they’re running with outdated cooling solutions. If your system is several years old, consider replacing the thermal paste and upgrading your cooling.
3. Faulty Hardware:
In rare cases, faulty CPUs or motherboards can fail when running heavy workloads like Cinebench. If you notice frequent crashes or instability when using Cinebench, it could be a sign that your hardware needs repair or replacement.
Best Practices for Using Cinebench Safely
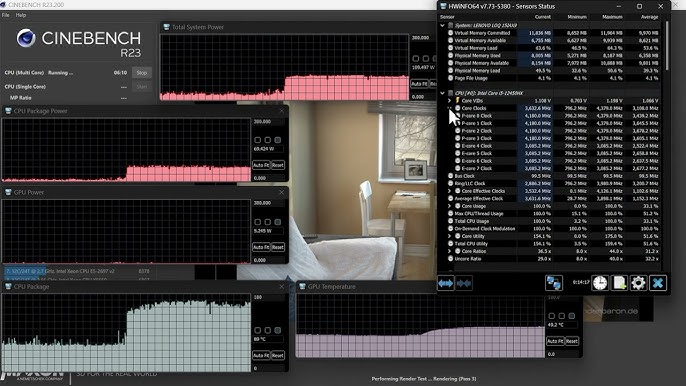
Monitor Temperatures:
Always monitor your CPU’s temperature when running Cinebench. Use free tools like HWMonitor or MSI Afterburner to track temperatures in real time. If your CPU exceeds 85°C, stop the test and check your cooling system.
Keep Your System Cool:
Ensure your PC has enough cooling, whether through air or liquid coolers. Clean your fans and ensure your system has good airflow to prevent heat buildup.
Be Careful with Overclocking:
If you’re new to overclocking, don’t push your CPU too far just for a higher Cinebench score. Overclocking increases the risk of overheating, so always ensure your cooling setup can handle the extra heat. Increase speeds gradually and stability test.
Don’t Run Cinebench in a Loop:
While a single run of Cinebench is fine, running it repeatedly without giving your CPU time to cool down can cause problems. Don’t treat Cinebench as a stress test – always allow your CPU to cool off between tests.
Keep Your System Updated:
Ensure your BIOS, drivers, and operating system are current. This helps improve system stability and performance and reduces the risk of problems during benchmarking.
How to Monitor CPU Temperatures During Cinebench?
Before running Cinebench, it’s wise to have temperature-monitoring tools in place. Popular tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or MSI Afterburner show real-time CPU temperatures, letting you see whether your cooling system is doing its job.
An ideal operating temperature for a CPU under a heavy load like Cinebench is around 70-85°C. If your CPU gets much hotter than that, it may be time to re-evaluate your cooling solution.
Read Also: Psu With 8 Pin And 4 Pin Cpu – Why It Matters!
Can Cinebench Cause Long-Term Wear and Tear on Your CPU?
While running Cinebench a few times won’t damage your CPU, repeated stress tests could shorten its lifespan. This happens due to thermal cycling, where your CPU’s constant heating and cooling can cause microscopic fractures in the silicon.
Fortunately, most modern CPUs are designed to handle thousands of thermal cycles without failure.
Cinebench vs. Other Benchmarking Tools
Cinebench:
- Purpose: Measures CPU performance by rendering a 3D scene.
- Test Type: Multi-core and single-core performance.
- Use Case: Ideal for content creators, 3D artists, and video editors.
- Duration: Short, typically under 10 minutes.
- Stress Level: Medium to high (short-term stress).
- Advantages: Focused on real-world applications (Cinema 4D), easy to use.
- Disadvantages: Limited in scope; doesn’t test extended stability or GPU performance.
Prime95:
- Purpose: Primarily used for stress testing CPU stability.
- Test Type: Multi-core stress test that generates maximum CPU load.
- Use Case: Ideal for overclockers and long-term stability testing.
- Duration: Long-term, can run for hours or even days.
- Stress Level: Extremely high (prolonged stress).
- Advantages: Excellent for testing stability under extreme loads.
- Disadvantages: It can cause very high temperatures and requires careful monitoring to avoid overheating.
Geekbench:
- Purpose: Measures both CPU and GPU performance.
- Test Type: Cross-platform performance evaluation with a variety of tasks.
- Use Case: Suitable for casual benchmarking across different devices.
- Duration: Short, usually under 5 minutes.
- Stress Level: Medium (general-purpose stress).
- Advantages: Cross-platform, quick tests, versatile benchmarks.
- Disadvantages: Less focused on specific tasks like 3D rendering or extreme stress.
AIDA64:
- Purpose: Comprehensive system diagnostics and benchmarking.
- Test Type: Multi-core CPU, memory, and GPU benchmarking.
- Use Case: Ideal for professionals looking for detailed system analysis.
- Duration: Customizable, can run long-term for stress testing.
- Stress Level: Medium to high (depending on test duration).
- Advantages: Detailed hardware diagnostics, can test various system components.
- Disadvantages: More complex to use, not as focused on a single component.
3DMark:
- Purpose: Focuses primarily on GPU performance but also includes CPU tests.
- Test Type: GPU-intensive with some CPU benchmarks (e.g., CPU Profile).
- Use Case: Best for gamers and those looking to test graphical performance.
- Duration: Short, usually around 10 minutes.
- Stress Level: Medium (depending on the selected test).
- Advantages: GPU-centric, useful for gaming performance evaluation.
- Disadvantages: Limited CPU stress compared to Cinebench or Prime95.
Blender Benchmark:
- Purpose: Measures CPU and GPU performance through rendering tasks.
- Test Type: 3D rendering with Blender software.
- Use Case: Great for content creators, 3D modelers, and animators.
- Duration: Depends on scene complexity (generally moderate).
- Stress Level: Medium to high (depending on task complexity).
- Advantages: Real-world performance for artists and designers.
- Disadvantages: It is not a general-purpose tool, and it is focused only on Blender tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the Cinebench temps for the 14700K?
The Intel Core i7-14700K typically reaches temperatures around 75-85°C during Cinebench benchmarks. Keeping your cooling system efficient can help maintain optimal performance.
2. Is Cinebench R23 safe to use for CPU benchmarking?
Yes, Cinebench R23 is safe for CPU benchmarking when used properly. Just ensure adequate cooling and monitor temperatures to avoid overheating during tests.
3. Where can I download Cinebench?
Cinebench can be downloaded from the official Maxon website or trusted software repositories. It’s available for Windows and macOS platforms.
4. How long should I run Cinebench to avoid CPU damage?
Running Cinebench for short bursts, typically 10 to 20 minutes, is ideal for testing without risking overheating. Constantly monitor temperatures to ensure your CPU stays within safe limits.
Conclusion:
Cinebench won’t harm your CPU but can cause overheating if your cooling isn’t adequate. To benchmark safely, keep an eye on temperatures and ensure your system has good airflow.
Read Also: