In computing, the central processing unit (CPU) is commonly known as the computer’s brain.However, like any high-performing component, the CPU generates heat as it works.When a CPU operates at 80 degrees Celsius, questions arise: Is this temperature safe? Does it affect performance? How can it be addressed?
A CPU at 80°C is safe during heavy tasks but close to high limits. Ensure proper cooling, clean airflow, and monitor to avoid long term damage.
Keep your CPU cool and performing at its best with these essential temperature management tips!
Table of Contents
What Does It Mean?
When your CPU reaches 80 degrees Celsius, it is operating in a high temperature range. While modern CPUs are designed to withstand temperatures up to 85-100 degrees Celsius.
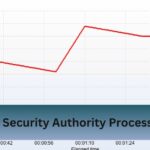
Consistently running at 80 degrees can signal underlying issues or indicate that the CPU is under heavy load, such as during gaming or video rendering.
Key points to note:
- Thresholds: Many CPUs have a maximum safe operating temperature, often listed in their specifications. Exceeding this threshold can trigger thermal throttling, where the CPU slows down to reduce heat.
- Temporary Spikes: Brief temperature spikes during intensive tasks are usually not harmful, but prolonged exposure can degrade performance over time.
Ideal CPU Temperature Ranges
- Idle Temperature: Around 30-40°C.
- Under Load: 60-80°C is usually safe.
- Critical Threshold: Most CPUs can tolerate up to 100°C briefly, but running at such high temperatures can quickly lead to problems.
These ranges can vary depending on the CPU model and manufacturer, so it’s always a good idea to check the specs for your specific processor.
Read Also: Is Anti Aliasing Cpu Or Gpu – A Simple Breakdown!
Is 80 Degrees Celsius Too Hot for Your CPU?
Typical CPU Temperature Thresholds:
Is 80°C safe? Yes—and no. For gaming and other intensive tasks, 80°C isn’t unusual and is generally within the safe range for most modern CPUs. However, if your CPU is hitting 80°C during light tasks or for extended periods, you might want to investigate further.
For instance, AMD and Intel CPUs often have thermal limits between 90°C and 100°C. While 80°C doesn’t breach this limit, it’s still uncomfortably close, especially for long-term use.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Effects of High CPU Temps:
High temperatures can cause thermal throttling, which means your CPU deliberately slows down to cool itself. This can reduce performance and lead to system instability.
Long-term exposure to high temperatures, on the other hand, can degrade your CPU over time. Components like thermal paste can dry out, and sustained heat can weaken the silicon itself, shortening the lifespan of your processor.
Common Causes of High CPU Temperatures
1. Insufficient Cooling:
Cooling is crucial for maintaining optimal CPU performance. If your cooling system is inadequate, temperatures can rise quickly. Common issues include:
- Stock coolers that are not powerful enough for high-performance CPUs.
- Malfunctioning fans or liquid cooling systems.
2. Poor Airflow in the Case:
A poorly ventilated computer case can trap hot air, preventing efficient cooling. Factors contributing to poor airflow include:
- Lack of intake and exhaust fans.
- Cables obstructing airflow paths.
3. Thermal Paste Issues:
Thermal paste is applied between the CPU and its cooler to enhance heat transfer. Problems arise when:
- Thermal paste has dried out.
- It was applied unevenly or insufficiently during installation.
4. Overclocking:
Overclocking pushes your CPU beyond its factory-set speed to enhance performance. Without adequate cooling, this leads to higher temperatures.
5. Dust Accumulation:
Over time, dust can accumulate inside your PC, clogging fans and heatsinks. This reduces cooling efficiency and causes temperatures to rise.
6. High Background Processes:
Excessive CPU usage from background applications or malware can keep the CPU running hotter than usual.
How to Reduce CPU Temperatures?
Improving Airflow in Your PC:
Proper airflow is crucial. Consider adding more case fans or optimizing their placement. A common setup includes intake fans at the front and exhaust fans at the back or top.Dust buildup is another big issue. Cleaning your PC regularly and organizing cables to improve airflow can make a world of difference.
Upgrading Your Cooling Solution:
If airflow improvements aren’t enough, upgrading your CPU cooler is the next step. Air coolers are affordable and effective for most users, while liquid cooling offers better performance for overclocked systems or high-end builds.
Software Optimization Techniques:
Using software like HWMonitor or Core Temp can help you keep an eye on your CPU’s temperature in real time. Many modern motherboards also let you adjust fan curves or undervolt your CPU, reducing heat output without sacrificing performance.
Read Also: Env Node Bad Cpu Type In Executable – How To Fix!
Monitoring and Maintaining CPU Temperatures
Tools for Monitoring CPU Temps:
There’s no shortage of tools for monitoring CPU temperatures. Some popular ones include:
- HWMonitor: A simple tool for tracking temperatures and voltages.
- MSI Afterburner: Ideal for gamers who want real-time performance stats.
- Core Temp: Lightweight and easy to use for beginners.
Preventive Measures for Long-Term CPU Health
- Choose the Right CPU Cooler: Investing in a high-quality cooler during the initial build can save you from temperature-related issues later.
- Plan Your PC Build for Airflow: Design your build with proper fan placement and cable management to optimize airflow.
- Maintain Regular Cleaning Schedules: Keeping your PC clean and dust-free prolongs the life of its components.
- Monitor Usage Patterns: Avoid running resource-heavy tasks for extended periods without sufficient cooling.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the maximum safe temperature for a CPU?
Most CPUs can handle up to 90-100°C, but it’s best to stay below 80°C for long-term health.
2. How can I tell if my CPU is overheating?
Look for signs like crashes, thermal throttling, or unusually high fan speeds.
3. Do gaming laptops naturally run hotter than desktops?
Yes, due to their compact design and limited cooling options.
4. Will using a laptop cooling pad help with high temperatures?
Absolutely! A cooling pad can improve airflow and reduce surface heat.
5. Is it safe to use software to undervolt my CPU?
Yes, undervolting is generally safe and can help lower temperatures without affecting performance.
Conclusion:
A CPU at 80°C is acceptable for heavy tasks but approaches critical limits. Maintain proper cooling, improve airflow, and monitor to prevent long term issues.
Read Also: