How to choose the right fan for your needs, and why these components play crucial roles in maintaining optimal system temperatures.
CHA fans optimize case airflow, keeping all components cool, while CPU fans target processor heat directly. Together, they ensure stable and efficient PC cooling.
CHA fan cools the whole case, and CPU fan saves your processor—team up for unbeatable PC performance!
Table of Contents
What is a CHA Fan?
Purpose and Functionality:
A CHA fan, a Chassis fan, or an SYS fan is primarily responsible for maintaining the airflow within your PC case.
It balances the intake and exhaust of air, ensuring that the internal components receive adequate cooling while expelling hot air out of the system.
Proper airflow helps prevent overheating and maintains a stable environment, which is essential for extending the lifespan of your hardware.
Placement and Usage:
Depending on your cooling configuration, CHA fans are typically mounted on the front, back, or top of the case.
Depending on their placement and cooling needs, these fans can be set to either pull cool air into the case (intake) or push hot air out (exhaust).
Connector Types:
Most CHA fans use a 3-pin connector, which allows the fan to run at a constant speed, irrespective of the system’s cooling requirements.
However, some modern CHA fans come with a 4-pin connector, which supports Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), enabling speed control based on system temperatures.
This feature allows for a more efficient and quieter cooling solution when the system is under varying loads(10Scopes).
Read Also: Cpu Maximum Frequency Always 100 – Tips and Tricks!
What is a CPU Fan?
Purpose and Functionality:
The CPU fan is dedicated to cooling your computer’s central processing unit (CPU), which generates the most heat in a system.
A CPU fan is typically attached directly to the CPU heatsink or used with a liquid cooling solution.
The fan’s primary role is ensuring that the CPU remains at a safe operating temperature, even during intensive gaming, video rendering, or multitasking tasks.
Connector and Header Requirements:
CPU fans usually require a 4-pin connector and are plugged into the CPU_FAN header on the motherboard.
This header is mandatory for most systems—if it’s not connected, many motherboards will halt the boot process to prevent potential damage from overheating.
The fourth pin on the CPU fan’s connector allows PWM speed control, which adjusts the fan’s RPM (rotations per minute) according to the CPU temperature, ensuring the most efficient cooling while minimizing noise(10Scopes).
Critical Differences Between CHA Fans and CPU Fans
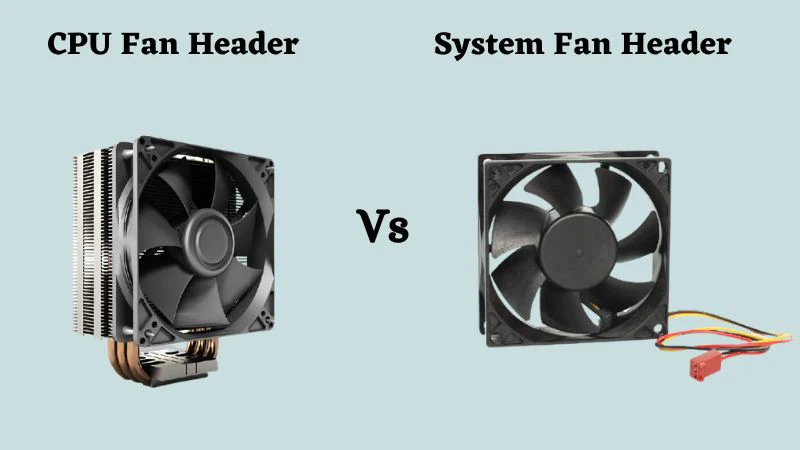

Header Compatibility and Pin Configuration:
One of the main differences between CHA fans and CPU fans is their pin configuration and the type of motherboard headers they connect to:
- CHA Fans: Often come with a 3-pin connector but can also have 4-pin configurations. CHA fans connect to the CHA_FAN or SYS_FAN headers.
- CPU Fans: Must have a 4-pin connector to allow for PWM speed control, ensuring precise cooling. They connect to the CPU_FAN header.
The pin configuration impacts fan speed control and how effectively each fan manages temperatures.
Placement and Role in Cooling Strategy:
- CHA Fans are responsible for overall case ventilation. They help regulate internal case temperatures by promoting proper airflow, ensuring all components receive adequate cooling.
- CPU Fans focus specifically on the CPU. Given the heat generated by the CPU, these fans must offer more precise cooling capabilities.
Speed and Control Mechanisms:
- CHA Fans: Depending on the pin configuration, they might not offer the same speed control as CPU fans. A 3-pin CHA fan will run at a constant speed, while a 4-pin fan allows speed adjustments based on temperature readings.
- CPU Fans: Generally operate at higher RPMs to provide sufficient cooling to the processor. They also utilize PWM for better speed control and quieter operation.
Size and Fin Design:
CPU fans tend to be smaller in diameter than CHA fans, as they need to operate at a faster speed to dissipate heat from the CPU efficiently.
In contrast, CHA fans are often more giant and designed to move air at a lower RPM, making them quieter.
Static Pressure vs. Airflow Optimization:
CPU fans often have a static pressure design, which is optimized to push air through resistive environments like heatsinks or radiators.
Conversely, CHA fans are typically airflow-optimized and designed to circulate air freely within the case(10Scopes).
Read Also: Can Cinebench Damage Cpu – Protecting Your Cpu!
Fan Bearing Types and Their Impact on Performance
The type of bearing used in a fan can affect its lifespan and noise level:
- Fluid Bearings: Inexpensive but have shorter lifespans. Suitable for horizontal mounting.
- Ball Bearings: Offer good longevity and are not affected by mounting orientation.
- Sleeve Bearings: More durable than fluid bearings but can degrade with excessive dust exposure.
- MagLev Bearings: Premium option with superior resistance to dust and shock.
Choosing the Right Fan for Your System
1. Determine the Placement and Role:
If you add or replace a fan for overall case ventilation, a CHA fan will be more suitable. If you want to enhance CPU cooling, a dedicated CPU fan or an all-in-one (AIO) cooler would be ideal.

2. Consider Compatibility with Your Motherboard:
Ensure that the fan’s connector type (3-pin or 4-pin) matches the available headers on your motherboard. While connecting a 3-pin fan to a 4-pin header is possible, you won’t have the same level of speed control.
3. Check the Size and Mounting Options:
Different cases and CPUs accommodate various fan sizes. Standard diameters for CHA fans include 120mm and 140mm, while CPU fans are generally smaller (92mm or 120mm). Ensure the fan you choose fits your case and has compatible mounting points.
4. Focus on Cooling Performance Metrics:
When comparing fans, two key metrics to consider are CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) and RPM (Rotations per Minute):
- CHA Fans: Typically have a lower RPM and CFM, making them quieter but less effective for targeted cooling.
- CPU Fans: Higher RPMs and CFM ratings help them provide adequate airflow to the CPU heatsink, keeping temperatures under control.
5. Hybrid Fans:
Many modern fans are designed as hybrids, capable of functioning as both CHA and CPU fans.
These fans often feature optimized fin designs that balance static pressure and airflow, making them versatile for various cooling configurations(10Scopes).
FAQs:
1. Can installing more CHA fans improve CPU cooling?
Yes, adding CHA fans improves overall case airflow, helping reduce ambient temperatures, which can, in turn, indirectly lower CPU temperatures.
2. Are CHA fans quieter than CPU fans?
Generally, yes. CHA fans often run at lower RPMs than CPU fans, making them quieter, but noise levels depend on the specific fan model and settings.
3. Do CHA and CPU fans require different power connectors?
Yes, CPU fans typically use a 4-pin connector for PWM control, while CHA fans can use either 3-pin or 4-pin connectors, depending on the model.
4. What happens if a CHA fan is plugged into a CPU fan header?
The CHA fan will work but might not provide precise cooling due to different voltage and speed control settings in CPU headers.
Conclusion:
CHA fans enhance airflow within the case, ensuring all components remain cool, while CPU fans focus specifically on dissipating heat from the processor. Together, they maintain stable and efficient cooling for your PC.
Read More: